£9.95 GBP, 2 hours
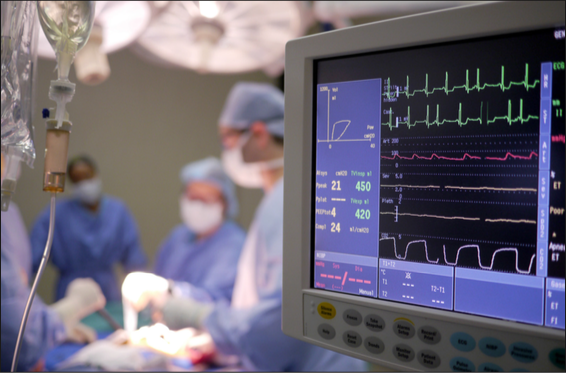
Measurement of end tidal carbon dioxide via capnography to monitor respiratory and metabolic function is standard practice in anaesthesia and becoming more common in intensive care units and during procedural sedation. End tidal carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring may also be used to assess effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Capnography is now emerging in general medical and surgical wards for monitoring of respiratory depression in patients using opioid analgesics.
Using end tidal CO2 (EtCO2) to monitor respiratory function offers many benefits over pulse oximetry. It is important to understand differences between these two monitoring methods, and why capnography is increasingly favoured in many situations. An understanding of the physiological processes involved in CO2 excretion allows nurses to use capnography in a safe and meaningful way while monitoring at risk patients in acute care.
After completing this activity and quiz you should be able to:
- Outline the production, transport, excretion and roles of CO2 in the body.
- Describe the significance of increased and decreased EtCO2 levels.
- Discuss the methods used to measure EtCO2, their advantages and disadvantages
- Compare the information provided by EtCO2 monitoring with pulse oximetry.